A microphone is the heart of Video or Audio systems and is used to convert sound into electrical signals.
In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell invented the microphone. The purpose of the Microphone is to convert sound into electrical signals.
However, the history of a wireless microphone is less old than a default microphone; the wireless microphone was invented in 1957. However, the availability of a Wireless microphone on a commercial level came in the 1990s.
Wireless microphones use radio frequency signals to transmit audio. This allows for greater freedom of movement and eliminates the need for cumbersome cords and cables. But how exactly do wireless microphones work?
In today’s article, we’ll discuss How Do Wireless Microphones Work in real life and provide a Detailed understanding of their functioning.
Quick Access
ToggleWhat is a Wireless Microphone?
A wireless microphone is a type of microphone which does not require a physical connection to the audio system or any other device. It uses radio waves to transmit audio signals and usually consists of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver.
The transmitter is the part that captures sound and converts it into an electrical signal, just like a traditional wired microphone. However, instead of sending this signal through a cable, it uses a built-in radio transmitter to send the signal wirelessly.
Conversely, the receiver picks up this radio signal and converts it into an electrical audio signal. This signal is sent to the audio system for further processing and amplification.
How Do Wireless Microphones Work?

To know How do wireless microphone work, you need to know what components need to work a wireless microphone.
You need a wireless microphone and a receiver to work a wireless microphone.
Let's have a look at How a wireless microphone build
As mentioned earlier, wireless microphones use radio frequency signals to transmit audio. And a Wireless microphone is built with four main components: a Microphone, a Preamplifier, a Transmitter, and an Antenna.
Microphone
The microphone is the part of the wireless system that captures sound and converts it into an electrical signal. It works similarly to a traditional wired microphone by using a diaphragm to convert sound waves into an electric current.
Preamplifier
The preamplifier boosts the electrical signal from the microphone to increase its strength, ensuring it can be transmitted wirelessly.
Transmitter

The transmitter is the heart of a wireless microphone. This component converts the amplified electrical signal into an electromagnetic radio wave using modulation. The radio wave carries the audio signal and transmits it to the receiver.
Antenna
The antenna is responsible for transmitting and receiving radio signals between the microphone and the receiver. It works
Receiver

The receiver serves as the endpoint in the wireless microphone system, and its primary role is to receive the radio waves sent by the antenna. It’s typically positioned near the audio system and is designed to pick up the transmitted signals without losing quality.
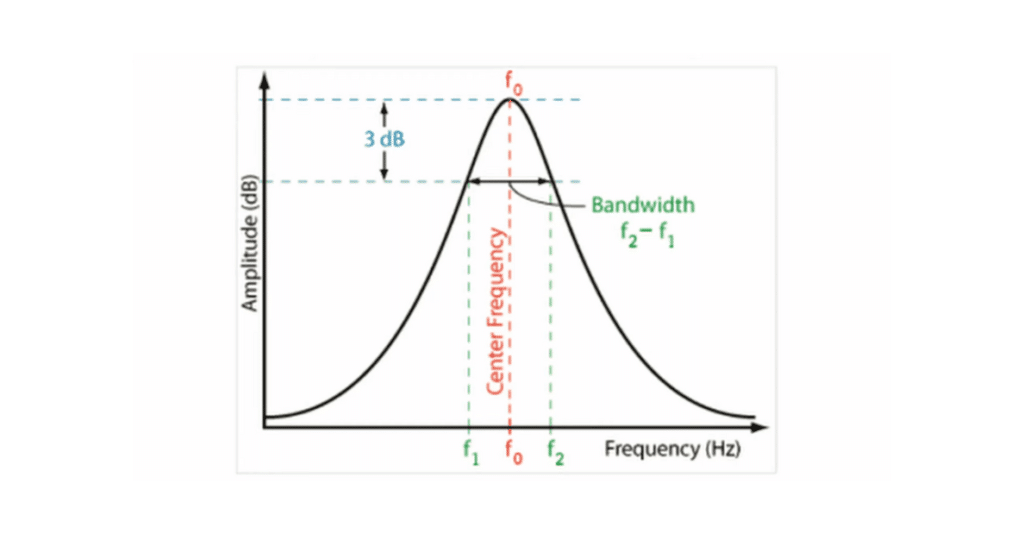
The first step in the process involves the receiver’s antenna capturing the transmitted radio waves. A built-in tuner within the receiver selects the desired frequency, effectively filtering out any potential interference or unwanted signals.
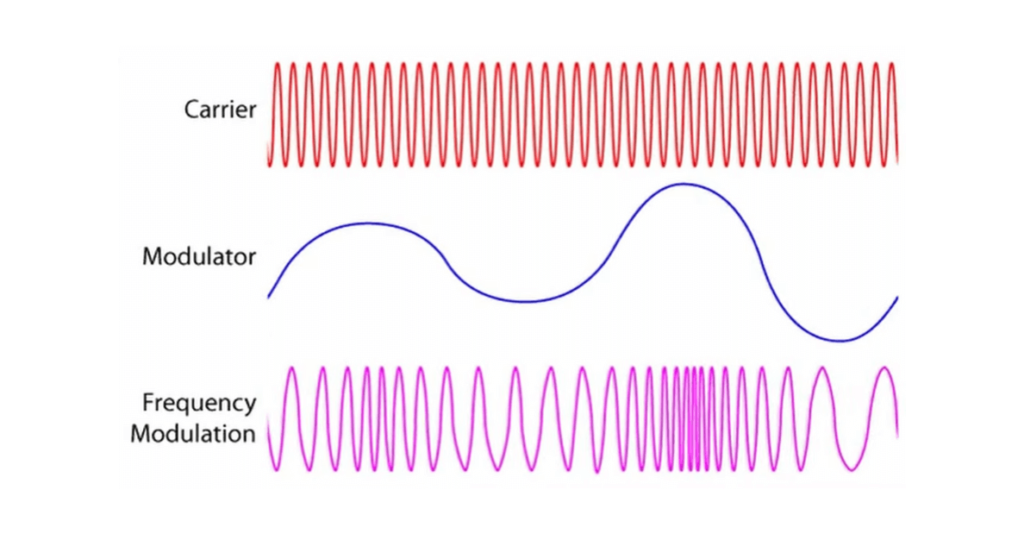
Once the radio signal is selected, the receiver demodulates it, essentially converting the radio wave back into an electrical audio signal. The demodulation process occurs in the receiver’s circuitry and is crucial for preserving the original audio quality.
Finally, the demodulated electrical signal is output to the connected audio system. This is usually done through a cable connection connecting the receiver to the audio system’s amplifier. Consequently, the original sound captured by the wireless microphone is reproduced and amplified for listeners to hear.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Wireless Microphone
Every electronic device must have its pros and cons. Wireless microphones are no different, and they have both advantages and disadvantages.
That is something you must know before shifting on a wireless microphone.
Advantages
- Mobility: The most significant advantage of wireless microphones is their freedom of movement. With no cords or cables restricting movement, performers can move freely on stage without worrying about tripping over cords.
- Convenience: Setting up a wireless microphone is significantly easier and quicker than setting up a wired microphone. This is particularly useful in significant events where multiple microphones are required.
- No tangling or cable issues: Cables can easily get tangled, damaged, or lost, resulting in inconvenience and additional costs. With wireless microphones, you eliminate the need for cables.
Disadvantages
- Interference: Wireless microphones rely on radio frequency signals to transmit audio, and they are susceptible to signal interference from other electronic devices such as cell phones or Wi-Fi routers.
- Limited range: Wireless microphones have a limited range due to the transmission of signals through radio waves. This can be problematic in large venues where performers must move far away from the receiver.
- Additional costs: Wireless microphones are more expensive than wired microphones, and they require different components, such as batteries and antennas, which can add to the overall cost.
Conclusion
I hope you found this article helpful in understanding how do wireless microphones work. They offer several advantages, such as mobility and convenience, but drawbacks, like interference and limited range.
Wireless microphones are widely used in various fields, from live performances to public speaking events. As technology advances, we can expect to see further improvements in the functionality and range of wireless microphones.
So, knowing how they work and their advantages and disadvantages is essential before choosing them for your specific needs.
So, confidently choose the right wireless microphone for your next event! Keep exploring and keep learning.
Thank You



